Leveraging Remote Sensing for National Security
In an era where threats to national security can emerge from anywhere, the importance of remote sensing technologies has skyrocketed. Imagine having the ability to monitor vast landscapes and detect potential threats from thousands of miles away; that’s the power of remote sensing. This article dives deep into how these technologies are not just futuristic concepts but are actively shaping our approach to national security. From surveillance of borders to disaster management and intelligence gathering, remote sensing is a game changer.
At its core, remote sensing is the science of collecting data about the Earth's surface without direct contact. Think of it as having a bird’s eye view of the world, primarily achieved through satellites and aerial sensors. These tools capture information in various forms, including images, temperature readings, and even chemical compositions. The principles behind remote sensing rely on the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with the Earth's surface; this interaction provides invaluable insights that are crucial for decision-making in national security.
When it comes to national security, one of the most significant applications of remote sensing is in the realm of surveillance. Governments worldwide leverage these technologies to monitor borders, detect illegal activities, and ensure the safety of their citizens. Imagine a high-tech security system that can spot suspicious movements even in the most remote areas—this is precisely what remote sensing offers. By utilizing advanced technologies, authorities can gather real-time data to make informed decisions and respond promptly to potential threats.
Border security is a critical area where remote sensing technologies shine. With the ability to provide real-time data on unauthorized movements, these tools are essential for safeguarding national boundaries. For instance, satellite imagery can cover vast stretches of land, allowing for the monitoring of areas that are otherwise difficult to patrol. This subsection examines specific tools and methods used in border security:
- Satellite Imagery: High-resolution images allow for effective surveillance and threat assessment.
- Aerial Drones: Drones equipped with remote sensing capabilities provide flexibility and precision in monitoring.
Satellite imagery is crucial for monitoring vast areas. The ability to capture high-resolution images allows security agencies to assess situations from a distance. These images can reveal patterns of movement, changes in land use, and even detect illegal activities such as smuggling or unauthorized crossings. By analyzing satellite data, authorities can make informed decisions about resource allocation and response strategies.
Drones equipped with remote sensing capabilities offer a level of flexibility and precision that is hard to match. These flying machines can be deployed quickly to areas of interest, providing real-time data and high-resolution images. Imagine a drone hovering over a border area, capturing live footage and sending it back to command centers for immediate analysis. This capability not only enhances surveillance but also improves intelligence gathering, making it a vital tool in national security.
In addition to surveillance, remote sensing plays a pivotal role in disaster management. During emergencies, having access to accurate and timely information can mean the difference between life and death. Remote sensing technologies provide critical data that aids in preparedness, response, and recovery efforts. For instance, satellite images can help identify areas affected by natural disasters, enabling emergency services to deploy resources efficiently and effectively. This section explores how these technologies streamline disaster management processes.
Remote sensing significantly enhances intelligence capabilities. The data collected through these technologies supports military operations and strategic planning. Imagine being able to gather intelligence from the comfort of a control room while monitoring activities across the globe. This section delves into how remote sensing data is integrated into military strategies, providing a comprehensive view of potential threats.
Geospatial analysis combines remote sensing data with geographic information systems (GIS). This powerful integration allows for in-depth analysis of spatial data, enhancing decision-making processes for national security. By visualizing data on maps, intelligence agencies can identify trends, patterns, and anomalies that may indicate potential threats. This subsection explains the importance of geospatial analysis in shaping national security strategies.
The integration of remote sensing technologies enables early threat detection. By continuously monitoring areas of interest, authorities can identify potential risks before they escalate. This proactive approach to security is akin to having a smoke detector in your home; it alerts you to danger before it becomes a crisis. This part discusses methods for identifying potential risks and enhancing situational awareness through advanced remote sensing techniques.
Q: How does remote sensing work?
A: Remote sensing works by collecting data about the Earth's surface using satellites, drones, and other aerial sensors. These tools capture various types of information, which is then analyzed for insights.
Q: What are the main applications of remote sensing in national security?
A: The main applications include surveillance of borders, disaster management, and intelligence gathering, all of which enhance national security efforts.
Q: How does satellite imagery contribute to border security?
A: Satellite imagery provides high-resolution images that help monitor large areas for unauthorized movements and illegal activities, enabling timely responses.
Q: What role do drones play in surveillance?
A: Drones equipped with remote sensing capabilities offer real-time monitoring and high-resolution imagery, allowing for flexible and precise surveillance.
Understanding Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is a fascinating and complex field that plays a crucial role in how we gather information about our planet. At its core, remote sensing involves collecting data about the Earth's surface from a distance, primarily utilizing satellites and aerial sensors. Imagine being able to see vast landscapes, monitor changes in the environment, or even track movements across borders, all from the comfort of a control room miles away. This is the power of remote sensing technology.
The basic principles of remote sensing revolve around the detection and measurement of electromagnetic energy reflected or emitted from objects on the Earth's surface. These measurements can tell us a lot about the characteristics of the land, water, and atmosphere. For instance, different materials reflect light differently; thus, by analyzing the reflected light, we can determine the type of vegetation, the presence of water bodies, or even the condition of urban infrastructure. This process is often enhanced by various technologies, including optical sensors, radar systems, and thermal imaging.
One of the most exciting aspects of remote sensing is its ability to provide data in real-time. With advancements in technology, we can now receive up-to-date information almost instantaneously. This capability is invaluable for applications in national security, where timely data can make the difference between safety and disaster. For example, when monitoring natural disasters, remote sensing can help assess the extent of damage and guide emergency response teams in their efforts to provide aid.
Remote sensing technologies can be categorized into two main types: active sensors and passive sensors. Active sensors emit their own signals and measure the reflected energy, while passive sensors detect natural energy that is reflected from the Earth's surface. Each type has its own unique advantages and applications. For instance, active sensors like radar can penetrate clouds and work in darkness, making them ideal for all-weather surveillance, whereas passive sensors are excellent for capturing detailed images of the Earth during daylight.
Furthermore, the integration of remote sensing with other technologies, such as geographic information systems (GIS), enhances its effectiveness. GIS allows users to visualize, analyze, and interpret spatial data, providing a comprehensive view of the information gathered through remote sensing. This combination is particularly powerful in decision-making processes related to national security, as it enables analysts to overlay various data layers and identify patterns or anomalies that may indicate threats.
In summary, understanding remote sensing is essential for appreciating its vast potential in national security applications. As technology continues to evolve, the capabilities of remote sensing will only expand, offering even more sophisticated tools for monitoring and protecting our nations. The future looks bright, and the possibilities are virtually endless!
- What is remote sensing? Remote sensing is the process of collecting data about the Earth's surface from a distance using satellites and aerial sensors.
- How does remote sensing contribute to national security? It enhances surveillance, disaster management, and intelligence gathering, providing critical information for decision-making.
- What are the types of remote sensing technologies? The main types are active sensors, which emit their own signals, and passive sensors, which detect natural energy.
- Can remote sensing be used in real-time? Yes, advancements in technology allow for near real-time data collection and analysis.
Applications in Surveillance
Remote sensing plays a vital role in enhancing national security through effective surveillance. Governments around the world are increasingly relying on these advanced technologies to monitor borders, detect illegal activities, and ensure public safety. Imagine having a bird’s-eye view of vast landscapes, allowing authorities to keep an eye on critical areas without being physically present. This capability not only improves response times but also enhances the overall effectiveness of security operations.
One of the most significant advantages of remote sensing in surveillance is its ability to provide real-time data. This means that security agencies can react promptly to any suspicious activities, which is crucial in preventing potential threats. For instance, if a government detects unusual movement near a border, they can quickly deploy resources to investigate further, potentially stopping illegal crossings or smuggling operations before they escalate.
When it comes to border security, remote sensing technologies are indispensable. They offer a comprehensive view of national boundaries, enabling authorities to monitor for unauthorized movements effectively. The integration of satellite imagery and aerial drones allows for a multi-faceted approach to surveillance. For example, satellite imagery can cover vast areas, while drones can zoom in on specific locations for detailed inspection.
Satellite imagery stands out as a cornerstone of remote sensing for surveillance. These high-resolution images provide critical insights into large expanses of land, making it easier to identify potential threats. With the ability to capture detailed visuals, authorities can assess changes in terrain, monitor infrastructure, and even track movements of individuals or vehicles that may pose a risk. The power of satellite imagery lies in its ability to offer a comprehensive overview of areas that are often difficult to access.
Aerial drones equipped with remote sensing capabilities have revolutionized the way surveillance is conducted. These versatile tools can cover ground quickly and provide real-time data that is essential for effective monitoring. Drones are particularly useful in situations where traditional surveillance methods may fall short, such as in dense urban environments or remote areas. Their agility allows for targeted reconnaissance, ensuring that security personnel can gather intelligence on-the-fly.
Moreover, drones can be equipped with various sensors, such as thermal imaging and multispectral cameras, which enhance their ability to detect illegal activities, such as poaching or drug trafficking. The flexibility and precision offered by drones make them a game-changer in the realm of national security.
In conclusion, the applications of remote sensing in surveillance are vast and impactful. By leveraging satellite imagery and aerial drones, governments can enhance their border security efforts, respond to threats more effectively, and ultimately ensure the safety of their citizens. As technology continues to evolve, the potential for remote sensing to safeguard national security only becomes more promising.
- What is remote sensing?
Remote sensing is the process of collecting data about the Earth's surface from a distance, using technologies such as satellites and aerial sensors.
- How does remote sensing enhance national security?
It provides real-time data for surveillance, aiding in border security, disaster management, and intelligence gathering.
- What are the main tools used in remote sensing?
The key tools include satellite imagery and aerial drones, which are utilized for monitoring and data collection.
- Why is real-time data important?
Real-time data allows security agencies to respond quickly to threats, enhancing their ability to prevent illegal activities and safeguard public safety.
Border Security
Border security is a paramount concern for any nation, as it directly impacts national safety and sovereignty. With the ever-increasing threats posed by illegal immigration, smuggling, and terrorism, governments are turning to remote sensing technologies to bolster their defenses. These advanced tools provide real-time data and situational awareness, allowing authorities to respond swiftly to potential threats. Imagine having eyes in the sky that can monitor vast stretches of land and sea, ensuring that every inch is accounted for. This is precisely what remote sensing offers.
One of the most effective methods in enhancing border security is through the use of satellite imagery. High-resolution images captured from space can provide detailed views of border areas, enabling security agencies to detect unusual patterns of movement. Whether it's tracking the flow of people across borders or identifying unauthorized vehicles, satellite imagery serves as a crucial component in maintaining border integrity. For instance, a recent analysis showed that regions monitored by satellites experienced a 30% reduction in illegal crossings due to the enhanced surveillance capabilities.
In addition to satellites, aerial drones have revolutionized border security efforts. Drones equipped with remote sensing technologies can cover challenging terrains that are difficult for ground patrols to access. These unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) provide flexibility and precision, allowing for targeted surveillance missions. Imagine a drone soaring above the rugged mountains or dense forests, capturing high-definition footage that can be analyzed in real-time. This capability not only improves response times but also ensures that authorities have the most accurate information at their fingertips.
Moreover, remote sensing technologies are not just about surveillance; they also facilitate data integration with other security systems. For example, combining satellite imagery and drone data with ground sensors can create a comprehensive picture of border activities. This integration allows for more informed decision-making and enhances the overall effectiveness of border security strategies. By leveraging these technologies, nations can create a multilayered defense mechanism that is both proactive and reactive.
In summary, remote sensing technologies are indispensable tools in the realm of border security. By utilizing satellite imagery and aerial drones, governments can monitor their borders more effectively, detect illegal activities, and respond to threats with unprecedented speed. As we continue to face evolving challenges in border security, it's clear that the integration of advanced technologies will play a crucial role in safeguarding national interests.
- What is remote sensing? Remote sensing is the process of collecting data about the Earth's surface from a distance, using satellites and aerial sensors.
- How does remote sensing enhance border security? Remote sensing provides real-time data and imagery that help monitor borders, detect illegal activities, and improve situational awareness.
- What types of remote sensing technologies are used for border security? Common technologies include satellite imagery and aerial drones equipped with advanced sensors.
- Can remote sensing help in disaster management? Yes, remote sensing plays a vital role in disaster management by providing critical information during emergencies, aiding in preparedness, response, and recovery efforts.
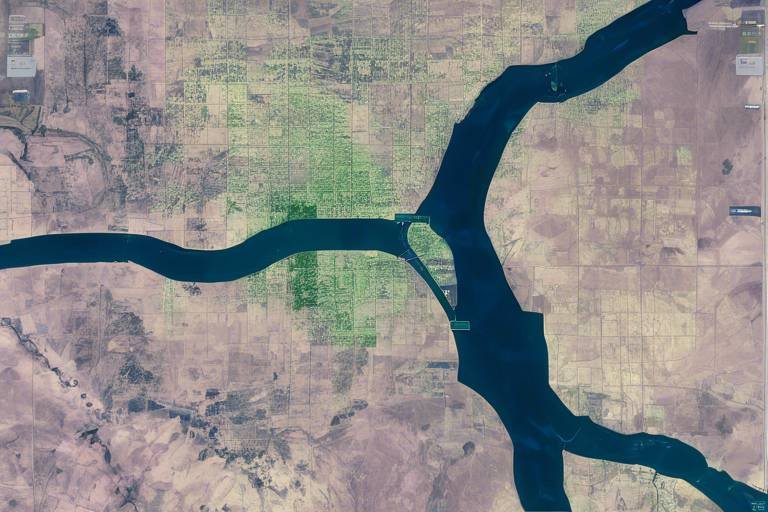
Satellite Imagery
When we think about national security, one of the most powerful tools at our disposal is . Imagine having a bird's-eye view of the entire nation, allowing us to monitor vast landscapes and detect changes in real-time. Satellite imagery provides high-resolution images that can capture details as small as a car parked in a remote area. This capability is not just a luxury; it’s a necessity for ensuring our borders are secure and our citizens are safe.
These images are obtained from satellites orbiting the Earth, equipped with advanced sensors that can detect various wavelengths of light. This means they can see not only in visible light but also in infrared and other spectrums. Such versatility allows for a range of applications, from tracking illegal activities to assessing damage after a natural disaster. The ability to capture images at different times enables analysts to observe changes over time, making it invaluable for monitoring environmental shifts or identifying suspicious activities.
Moreover, the technology behind satellite imagery has evolved rapidly. Today, we have access to high-resolution satellite imagery that can provide detailed views of urban areas, forests, and even remote terrains. For example, satellites like WorldView-3 can capture images with a resolution of up to 31 centimeters. This level of detail is crucial for effective surveillance and threat assessment. The images can be processed and analyzed using advanced software, allowing officials to create detailed maps and models that inform strategic decisions.
Let’s break down some of the key advantages of utilizing satellite imagery in national security:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Satellites can provide near real-time data, which is essential for timely decision-making.
- Wide Coverage: They can monitor large geographical areas that would be impossible to cover with ground-based surveillance.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Although the initial investment in satellite technology can be high, the long-term savings in manpower and resources can be significant.
- Data Integration: Satellite images can be integrated with other data sources, enhancing the overall analysis.
In conclusion, the role of satellite imagery in national security cannot be overstated. It serves as a crucial component for effective surveillance, enabling governments to keep a watchful eye over their territories and respond swiftly to any threats. As technology continues to advance, the potential for satellite imagery to enhance our national security efforts will only grow, making it an indispensable tool in our arsenal.
Q1: How often do satellites capture images of the Earth?
A: Satellites can capture images multiple times a day, depending on their orbit and the specific mission. Some satellites are designed for frequent revisits, providing near real-time data.
Q2: What types of data can satellite imagery provide?
A: Satellite imagery can provide a range of data, including land use, vegetation health, urban development, and even temperature variations, depending on the sensors used.
Q3: How is satellite imagery used in disaster management?
A: In disaster management, satellite imagery helps assess damage, track recovery efforts, and plan for future emergencies by providing critical information during and after events like floods or earthquakes.
Q4: Are there privacy concerns associated with satellite imagery?
A: Yes, there are privacy concerns, as high-resolution images can capture private properties and activities. Balancing national security needs with individual privacy rights is an ongoing discussion.
Aerial Drones
Aerial drones have revolutionized the way we approach national security and surveillance. These unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are equipped with advanced remote sensing technologies that allow them to gather data and monitor areas that might be difficult or dangerous for human operatives to access. Imagine having an eye in the sky that can provide real-time information from a vantage point that is both safe and strategic. Drones are not just flying cameras; they are sophisticated tools that can analyze terrain, detect movements, and even identify potential threats with remarkable precision.
One of the most significant advantages of using aerial drones in surveillance is their flexibility. Unlike traditional aircraft, drones can be deployed quickly and at a fraction of the cost. They can fly at lower altitudes, which allows them to capture high-resolution images and videos that are crucial for making informed security decisions. For instance, during border monitoring operations, drones can patrol vast stretches of land, providing live feeds to security personnel who can respond to incidents as they unfold.
Moreover, the data collected by drones can be processed and analyzed using advanced software, enhancing their utility in national security efforts. Drones can be equipped with various sensors, including thermal imaging and infrared cameras, to detect heat signatures or movements that would otherwise go unnoticed. This capability is particularly useful in scenarios such as:
- Search and Rescue Operations: Drones can quickly locate missing persons in challenging terrains.
- Monitoring Natural Disasters: They provide real-time data to assess damage and coordinate relief efforts.
- Surveillance of High-Risk Areas: Drones can monitor regions prone to illegal activities, such as smuggling or human trafficking.
Another key feature of aerial drones is their autonomous flight capabilities. Many modern drones can be programmed to follow specific flight paths or respond to certain triggers without direct human control. This autonomy allows for prolonged surveillance missions, as drones can operate for hours while collecting valuable data. Additionally, their ability to integrate with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), further enhances their effectiveness. AI can analyze the data collected by drones, identifying patterns and anomalies that could indicate potential threats.
In summary, aerial drones represent a significant advancement in the realm of national security. Their ability to provide real-time surveillance, collect detailed data, and operate autonomously makes them invaluable assets in safeguarding our borders and public safety. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect drones to play an even more prominent role in enhancing our security measures, ensuring that we stay one step ahead of potential threats.
- What types of sensors can be equipped on aerial drones? Drones can carry various sensors, including optical cameras, thermal imaging cameras, and LiDAR systems, to gather diverse data types.
- How do drones contribute to disaster response? Drones provide real-time imagery and data, which help in assessing damage, locating victims, and coordinating rescue operations effectively.
- Are there legal restrictions on drone usage for surveillance? Yes, drone usage is subject to regulations that vary by country, including privacy laws and airspace restrictions.
Disaster Management
When disaster strikes, every second counts. In such critical moments, remote sensing technologies become invaluable allies in managing emergencies effectively. Imagine a world where we can predict natural disasters before they happen, or respond to them with pinpoint accuracy. Remote sensing allows us to gather crucial information about affected areas, enabling governments and organizations to act swiftly and efficiently. By utilizing data from satellites and aerial sensors, we can monitor environmental changes, assess damage, and coordinate relief efforts seamlessly.
One of the most significant advantages of remote sensing in disaster management is its ability to provide real-time data. For instance, during a flood, satellite imagery can reveal the extent of the inundation, helping emergency responders prioritize their actions. Similarly, in the aftermath of an earthquake, aerial drones can quickly survey damaged infrastructures, identifying areas that require immediate attention. This rapid assessment is crucial for deploying resources effectively and ensuring that help reaches those in need as soon as possible.
Moreover, remote sensing technologies contribute to disaster preparedness. By analyzing historical data and patterns, authorities can identify high-risk areas and develop mitigation strategies. For example, geospatial analysis can help in mapping flood-prone regions, allowing communities to establish early warning systems and evacuation plans. This proactive approach not only saves lives but also minimizes economic losses.
Consider the role of remote sensing in wildfires. Satellites equipped with thermal imaging can detect hotspots, providing early warnings to firefighting teams. This capability allows for quicker mobilization of resources, potentially preventing a small fire from escalating into a catastrophic blaze. In essence, remote sensing acts as the eyes in the sky, offering a comprehensive view of the situation on the ground.
To further illustrate the impact of remote sensing in disaster management, here’s a table summarizing its key applications:
| Application | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Flood Monitoring | Real-time satellite imagery to track flood extents | Improved resource allocation and evacuation planning |
| Earthquake Assessment | Aerial surveys to evaluate damage | Quick identification of areas in need of urgent assistance |
| Wildfire Detection | Thermal imaging to identify hotspots | Early intervention to prevent large-scale disasters |
| Hurricane Tracking | Satellite data to predict storm paths | Enhanced preparedness and response strategies |
In conclusion, the integration of remote sensing into disaster management not only enhances our ability to respond to emergencies but also equips us with the tools to mitigate future risks. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated applications that will further revolutionize how we manage disasters. The future of disaster management is undoubtedly bright, with remote sensing leading the charge.
- What is remote sensing? Remote sensing is the process of collecting data about the Earth's surface from a distance, typically using satellites or aerial sensors.
- How does remote sensing help in disaster management? It provides real-time data, enables rapid assessment of damage, and supports preparedness and mitigation strategies.
- Can remote sensing predict natural disasters? While it cannot predict disasters with certainty, it can analyze historical data and patterns to identify high-risk areas.
- What technologies are used in remote sensing? Technologies include satellites, aerial drones, and various imaging techniques such as thermal and multispectral imaging.
Intelligence Gathering
In today's complex geopolitical landscape, has become a cornerstone of national security. The integration of remote sensing technologies into intelligence operations is not just a luxury; it's a necessity. Imagine trying to navigate a dense forest without a map or compass—this is what intelligence agencies would face without the precise data provided by remote sensing. These technologies allow for the collection of vast amounts of information from a distance, enabling governments to make informed decisions that can mean the difference between safety and vulnerability.
Remote sensing significantly enhances intelligence capabilities by providing real-time data that can be used for strategic planning and military operations. For instance, satellite imagery can reveal troop movements, infrastructure developments, and even environmental changes that may indicate brewing conflicts. The ability to visualize these elements in a timely manner allows for proactive measures rather than reactive responses, which is crucial in maintaining national security.
One of the most fascinating aspects of remote sensing in intelligence gathering is its ability to conduct geospatial analysis. This process involves the combination of remote sensing data with Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to create visual representations of data that can be easily interpreted. Imagine having a 3D map that not only shows where a potential threat is located but also provides insights into the terrain, population density, and even weather conditions. This level of detail is invaluable for decision-makers who need to act quickly and effectively.
Furthermore, the integration of remote sensing technologies enables early threat detection. By continuously monitoring areas of interest, intelligence agencies can identify potential risks before they escalate. For example, changes in land use patterns detected through satellite imagery can signal the establishment of illegal facilities or military installations. This proactive approach to threat detection enhances situational awareness and allows for timely interventions.
To illustrate the impact of remote sensing on intelligence gathering, consider the following table that summarizes key technologies and their applications:
| Technology | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Satellite Imagery | Monitoring troop movements and infrastructure | High-resolution images for detailed analysis |
| Aerial Drones | Real-time surveillance and reconnaissance | Flexibility and precision in data collection |
| Geospatial Analysis | Mapping and visualizing data for decision-making | Enhanced situational awareness and strategic planning |
| Remote Sensing Sensors | Detecting environmental changes and threats | Early warning capabilities for potential risks |
In conclusion, the role of remote sensing in intelligence gathering cannot be overstated. It equips national security agencies with the tools necessary to navigate the complexities of modern threats. By leveraging these technologies, governments can enhance their situational awareness, make informed decisions, and ultimately safeguard their citizens. As we move forward, the evolution of remote sensing technologies will undoubtedly continue to shape the landscape of intelligence gathering, making it more efficient and effective than ever before.
- What is remote sensing? Remote sensing is the process of collecting data about the Earth's surface from a distance, primarily using satellites and aerial sensors.
- How does remote sensing aid in intelligence gathering? It provides real-time data that helps in monitoring activities, detecting threats, and making strategic decisions.
- What are some key technologies used in remote sensing? Technologies include satellite imagery, aerial drones, and geospatial analysis tools.
- Why is early threat detection important? Early detection allows for proactive measures to be taken, reducing the risk of escalation and enhancing national security.
Geospatial Analysis
Geospatial analysis is a game changer when it comes to enhancing national security. It’s like having a powerful magnifying glass that allows decision-makers to see not just the surface of a situation but the underlying patterns and trends that can inform strategic actions. By integrating remote sensing data with Geographic Information Systems (GIS), governments and security agencies can visualize complex data in a way that makes it easier to understand and act upon. Imagine trying to solve a jigsaw puzzle without knowing what the final picture looks like; geospatial analysis provides that crucial context, enabling a clearer understanding of the threats we face.
This analysis involves various techniques that help in interpreting spatial data, which is collected from satellites, drones, and other remote sensing technologies. By layering different types of data—such as terrain, population density, and infrastructure—analysts can create comprehensive maps that reveal critical insights. For instance, during a natural disaster, geospatial analysis can pinpoint areas that are most at risk, allowing for more effective resource allocation and emergency response strategies.
Moreover, the role of geospatial analysis extends beyond just immediate threats. It can also assist in long-term strategic planning. For example, military operations can leverage this technology to identify potential enemy movements or to assess the impact of geopolitical changes in a region. The ability to visualize potential scenarios helps military leaders prepare for various contingencies, making geospatial analysis a vital tool in the arsenal of national security.
To give you a clearer picture of how geospatial analysis is applied in national security, consider the following key components:
- Data Integration: Combining various datasets from remote sensing technologies to create a unified view of the situation.
- Predictive Modeling: Using historical data to forecast future events or trends that could impact national security.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuously updating geospatial data to reflect current conditions and threats.
In summary, geospatial analysis is not just a technical process; it is a crucial element of national security strategy that empowers agencies to make informed decisions. By leveraging the power of remote sensing and GIS, we can enhance our situational awareness and respond more effectively to the ever-evolving landscape of threats. As we continue to develop and refine these technologies, the potential for improving our national security capabilities will only grow stronger.
- What is geospatial analysis? Geospatial analysis is the process of gathering, displaying, and manipulating imagery, GPS, satellite photography, and historical data to understand spatial relationships and patterns.
- How does remote sensing contribute to geospatial analysis? Remote sensing provides the raw data needed for geospatial analysis, including satellite imagery and aerial photography, which are essential for mapping and monitoring changes over time.
- What are some applications of geospatial analysis in national security? Applications include border security monitoring, disaster response planning, intelligence gathering, and military strategic planning.
Threat Detection
In today's world, where uncertainty looms large, the ability to detect threats early can be the difference between safety and catastrophe. Remote sensing technologies have revolutionized the way we approach threat detection, providing us with tools that are not just reactive but also proactive. Imagine a watchful eye in the sky, constantly scanning for anomalies and potential dangers. This is precisely what remote sensing does—it offers a comprehensive overview of vast areas, allowing for the identification of suspicious activities before they escalate into serious threats.
One of the most significant advantages of remote sensing in threat detection is its capacity to monitor large geographic regions in real-time. By utilizing advanced algorithms and data analytics, authorities can sift through massive datasets to pinpoint unusual patterns. For instance, if a specific area shows a sudden increase in human activity during odd hours, this could trigger alerts for further investigation. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with remote sensing data enhances this capability, enabling systems to learn from previous incidents and improve their predictive accuracy.
Moreover, remote sensing technologies can be employed to detect various types of threats, including:
- Environmental Threats: Changes in land use, deforestation, and pollution can all be monitored through satellite imagery, helping to identify potential hazards that could lead to disasters.
- Military Threats: The movement of troops and military equipment can be tracked, providing critical intelligence for strategic planning.
- Terrorism: Unusual patterns of movement in sensitive areas can indicate potential terrorist activities, allowing for preemptive measures to be taken.
Furthermore, the use of geospatial analysis plays a crucial role in enhancing threat detection capabilities. By combining remote sensing data with Geographic Information Systems (GIS), analysts can visualize data in a spatial context, making it easier to identify trends and hotspots. This integration not only aids in immediate threat detection but also assists in long-term strategic planning, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently to areas of highest risk.
In conclusion, the integration of remote sensing technologies into national security frameworks allows for a more dynamic and responsive approach to threat detection. With the ability to monitor vast areas in real-time, analyze complex data, and predict potential risks, these technologies empower governments and security agencies to act swiftly and decisively in the face of danger. As we continue to advance in this field, the potential for improved safety and security is not just promising; it is essential.
- What is remote sensing? Remote sensing is the collection of data about the Earth's surface from a distance, often using satellites or aerial sensors.
- How does remote sensing help in national security? It enhances surveillance, disaster management, and intelligence gathering, allowing for better threat detection and response.
- What are some applications of remote sensing in threat detection? Applications include monitoring military movements, detecting environmental hazards, and identifying potential terrorist activities.
- How does geospatial analysis improve threat detection? It combines remote sensing data with GIS to visualize information spatially, aiding in identifying trends and hotspots.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is remote sensing?
Remote sensing is the process of collecting data about the Earth's surface from a distance, primarily using satellites and aerial sensors. It allows for the observation and analysis of physical features and changes on the planet without direct contact.
- How does remote sensing enhance national security?
Remote sensing enhances national security by providing critical data for surveillance, disaster management, and intelligence gathering. It enables governments to monitor borders, detect illegal activities, and respond effectively to emergencies.
- What role do satellites play in surveillance?
Satellites provide high-resolution imagery that is essential for monitoring large areas. They help in assessing threats, tracking movements, and ensuring that borders are secure from unauthorized activities.
- How are drones used in remote sensing?
Drones equipped with remote sensing technology offer flexibility and precision in surveillance. They can be deployed for real-time monitoring, providing valuable intelligence in areas that are difficult to access.
- What is the significance of geospatial analysis?
Geospatial analysis combines remote sensing data with geographic information systems (GIS) to enhance decision-making processes. It allows for better understanding of spatial relationships and trends, which is crucial for national security planning.
- How does remote sensing aid in disaster management?
Remote sensing provides critical information during emergencies, helping in preparedness, response, and recovery efforts. It allows for real-time assessment of disaster-affected areas, enabling quicker and more effective action.
- What methods are used for threat detection?
Threat detection methods include analyzing satellite imagery, utilizing drone surveillance, and integrating data from various remote sensing technologies. This combination allows for early identification of potential risks and enhances situational awareness.
- Can remote sensing be used for environmental monitoring?
Absolutely! Remote sensing is widely used for environmental monitoring, including tracking deforestation, assessing land use changes, and monitoring climate change effects. It provides valuable data for sustainable management practices.