Real-Time Intelligence - The Role of Satellites in Modern Warfare
In today's fast-paced world, the battlefield has evolved far beyond the traditional front lines. Real-time intelligence is now a game changer, and satellites are at the forefront of this technological revolution. Imagine a chess game where every move is monitored in real-time, allowing players to anticipate and counter their opponent's strategies. This is precisely how modern warfare operates, with satellites providing critical information that shapes military decisions and actions. Through the lens of satellite technology, military operations have transformed from reactive to proactive, enabling forces to stay one step ahead of their adversaries.
Understanding the fundamentals of satellite technology is crucial for grasping its impact on warfare. Satellites are not just shiny objects orbiting the Earth; they are sophisticated tools that gather and relay information. There are various types of satellites, each serving unique functions in military applications. For instance, reconnaissance satellites are designed to capture high-resolution images of enemy territories, while communication satellites ensure seamless connectivity between troops in remote locations. The integration of these technologies creates a comprehensive picture of the battlefield, allowing military strategists to make informed decisions.
Real-time data collection through satellites allows for immediate intelligence gathering, which is vital in combat scenarios. Think about it: in the heat of battle, every second counts. Having access to timely information can mean the difference between victory and defeat. When troops receive real-time updates about enemy movements or potential threats, they can adjust their strategies on the fly, enhancing their operational effectiveness. The ability to monitor and analyze data instantaneously empowers commanders to make swift decisions, ensuring that military operations are not just reactive but also strategically planned.
Different types of intelligence, including imagery, signals, and electronic intelligence, are collected by satellites. Each type plays a unique role in shaping military strategy and tactics. For example, imagery intelligence (IMINT) provides visual insights into enemy positions, while signals intelligence (SIGINT) focuses on intercepting communications to understand enemy plans. The integration of these intelligence types creates a multi-faceted view of the battlefield, allowing military leaders to devise strategies that are both comprehensive and effective.
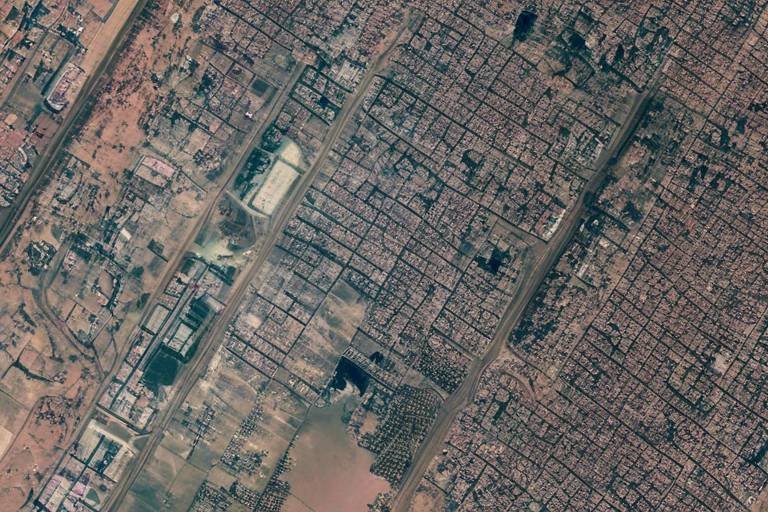
Imagery intelligence involves capturing visual data from satellite imagery, providing critical insights into enemy positions and terrain. Imagine having a bird's-eye view of the battlefield; this is what IMINT offers. It allows military personnel to assess the landscape, identify potential obstacles, and locate enemy assets. This information is invaluable during reconnaissance missions, where understanding the environment can lead to successful operations. By analyzing satellite images, commanders can make informed decisions about troop movements and resource allocation, ultimately enhancing mission success rates.
Signals intelligence focuses on intercepting and analyzing communications. In a world where information is power, SIGINT is like having a secret decoder ring that reveals enemy intentions. By monitoring radio transmissions, satellite communications, and even internet traffic, military forces can gain insights into enemy operations and strategies. This intelligence enhances situational awareness, allowing troops to anticipate enemy actions and counter them effectively. In essence, SIGINT acts as an early warning system, providing critical information that can shape the outcome of military engagements.
The integration of satellite intelligence with ground forces is essential for coordinated operations. Picture a symphony orchestra; each instrument must play in harmony to create a beautiful piece of music. Similarly, real-time data from satellites allows ground forces to execute tactical maneuvers with precision. When soldiers on the ground receive live updates about enemy positions, they can adjust their strategies accordingly, ensuring that every move is calculated and effective. This seamless communication between air and ground forces enhances battlefield coordination, leading to more successful outcomes in military operations.
Despite its advantages, satellite intelligence faces challenges such as vulnerability to cyberattacks and adverse weather conditions. Just like a ship navigating through a storm, satellites must withstand various obstacles that can disrupt their functionality. Cybersecurity threats pose significant risks to satellite operations. Adversaries may attempt to intercept communications or jam signals, potentially crippling military capabilities. Therefore, securing satellite communications is paramount to maintaining operational integrity.
Cybersecurity threats pose significant risks to satellite operations. As military reliance on satellite technology increases, so does the potential for cyberattacks from adversaries. These attacks can disrupt communication channels, leading to information loss or miscommunication on the battlefield. Protecting satellite systems against these threats is crucial for maintaining a strategic advantage. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures ensures that military operations remain secure and effective, safeguarding sensitive information from falling into enemy hands.
Adverse weather conditions can hinder satellite functionality and data accuracy. Heavy clouds, storms, or even solar flares can obstruct satellite signals, leading to gaps in intelligence. This unpredictability poses a challenge for military operations that rely heavily on satellite data. To mitigate these effects, military forces continuously invest in advanced technologies and strategies, ensuring that even in unfavorable conditions, they can maintain a level of situational awareness. This adaptability is essential for success in modern warfare.
The future of warfare will increasingly rely on advanced satellite technology. Emerging trends such as miniaturization of satellites, improved data processing capabilities, and the integration of artificial intelligence are set to revolutionize military operations. As we look ahead, it's clear that satellites will play an even more critical role in shaping the strategies of tomorrow's conflicts. The ability to gather and analyze vast amounts of data in real-time will empower military forces to respond to threats with unprecedented speed and precision.
- How do satellites gather intelligence? Satellites gather intelligence through various means, including capturing imagery, intercepting signals, and analyzing electronic communications.
- What are the main types of satellite intelligence? The main types of satellite intelligence include imagery intelligence (IMINT) and signals intelligence (SIGINT).
- What challenges do satellites face in military operations? Satellites face challenges such as cybersecurity threats and adverse weather conditions that can impact their functionality.
- How is satellite intelligence integrated with ground forces? Satellite intelligence is integrated with ground forces through real-time data sharing, enhancing coordination and operational effectiveness.
Satellite Technology Overview
Understanding the fundamentals of satellite technology is crucial for grasping its impact on warfare. Satellites are not just fancy gadgets orbiting the Earth; they are the backbone of modern military operations, providing a wealth of information that can turn the tide of battle. Imagine being able to see the battlefield from above, gathering data in real-time, and making informed decisions based on that information. This is the power of satellite technology in contemporary warfare.
There are several types of satellites, each serving a unique purpose in military applications. The two primary categories are Earth observation satellites and communication satellites. Earth observation satellites are equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors that can capture detailed images and data about the Earth's surface. They play a pivotal role in reconnaissance missions, allowing military planners to monitor enemy movements and assess the terrain. Communication satellites, on the other hand, facilitate secure and instantaneous communication between troops on the ground and command centers far away. This seamless flow of information is vital for coordinated operations.
To give you a clearer picture, here's a breakdown of the key types of military satellites:
| Satellite Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Earth Observation Satellites | Capture images and data for reconnaissance and surveillance |
| Communication Satellites | Enable secure communication between military units |
| Navigational Satellites | Provide GPS services for accurate positioning and navigation |
| Weather Satellites | Monitor weather conditions to support military planning |
Moreover, satellites can be equipped with various sensors that allow them to gather different types of intelligence. For instance, some satellites are designed to detect electromagnetic signals, which can provide insights into enemy communications and radar systems. Others might focus on infrared technology to spot heat signatures, making them invaluable for locating hidden assets or tracking troop movements at night.
In essence, the integration of these technologies enhances the military's ability to operate effectively in diverse environments. As we delve deeper into the role of satellites in modern warfare, you'll see how they are not just tools but essential components that shape military strategy and tactics. The advancements in satellite technology continue to evolve, promising even greater capabilities for future military operations.
- What are the main types of military satellites? Military satellites can be categorized into Earth observation, communication, navigational, and weather satellites, each serving distinct functions.
- How do satellites enhance military operations? Satellites provide real-time data and communication, enabling better decision-making and coordination among military units.
- What challenges do satellites face in military applications? Satellites are vulnerable to cyberattacks and can be affected by adverse weather conditions, which can hinder their functionality.
Real-Time Data Collection
Imagine being able to see the battlefield from above, with every movement and strategy laid bare in real-time. This is the power of through satellites, a game-changer in modern warfare. The ability to gather immediate intelligence is not just a luxury; it's a necessity that can mean the difference between victory and defeat. In combat scenarios, timely information can significantly influence decision-making processes, allowing commanders to adapt their strategies on the fly and respond to evolving threats.
Satellites equipped with advanced sensors and imaging technology are capable of collecting a vast array of data. This information can include everything from troop movements to environmental changes, offering a comprehensive view of the operational landscape. With the right data at their fingertips, military leaders can make informed decisions that enhance operational effectiveness and minimize risks.
One of the most crucial aspects of real-time data collection is its ability to integrate various types of intelligence. For instance, satellites can simultaneously gather Imagery Intelligence (IMINT) and Signals Intelligence (SIGINT), providing a multi-faceted understanding of the battlefield. This integration allows for a more nuanced approach to military strategy, where every detail counts. The synergy between different intelligence types creates a robust framework for situational awareness, enabling ground forces to execute coordinated maneuvers with precision.
Moreover, the speed at which data is collected and transmitted is vital. In a world where every second counts, delays can lead to missed opportunities or, worse, catastrophic outcomes. Satellites ensure that the flow of information is swift and continuous, allowing military units to remain one step ahead of their adversaries. This real-time connectivity is akin to having a tactical advisor in the sky, constantly feeding critical insights to ground forces.
However, the benefits of real-time data collection come with their own set of challenges. The sheer volume of data generated can be overwhelming, necessitating advanced algorithms and AI systems to process and analyze the information efficiently. Furthermore, the need for secure communication channels cannot be overstated. As military operations become increasingly reliant on satellite intelligence, ensuring that this data remains secure from cyber threats is paramount.
In summary, real-time data collection through satellites is revolutionizing military operations. By providing immediate access to vital intelligence, satellites enhance decision-making, improve tactical maneuvers, and ultimately increase the chances of success on the battlefield. As technology continues to evolve, the role of satellites in warfare will only become more pronounced, making it essential for military forces to adapt and integrate these tools into their operational strategies.
- What types of data can satellites collect in real-time? Satellites can collect various types of data, including imagery, signals, and environmental information, which are crucial for military operations.
- How does real-time data collection enhance military strategy? By providing immediate intelligence, real-time data collection allows commanders to make informed decisions and adapt strategies quickly in response to battlefield dynamics.
- What challenges does real-time data collection face? Challenges include data overload, the need for secure communication, and vulnerability to cyber threats.
Types of Intelligence Gathered
In the complex landscape of modern warfare, the types of intelligence gathered by satellites play a pivotal role in shaping military strategies and operations. These satellites are equipped with advanced technologies that allow them to collect various forms of intelligence, each with its unique contribution to the battlefield. Understanding these types not only highlights the capabilities of satellite technology but also underscores its significance in enhancing situational awareness for military forces.
One of the primary types of intelligence is Imagery Intelligence (IMINT). This involves capturing visual data through high-resolution images taken from space. IMINT provides critical insights into enemy positions, movements, and the geography of the battlefield. For instance, during reconnaissance missions, military planners rely heavily on satellite imagery to assess the terrain and identify potential threats. The clarity and detail of satellite images can reveal hidden installations or troop concentrations that might otherwise go unnoticed. This visual intelligence is akin to having an eagle's eye, soaring high above to provide a panoramic view of the battlefield.
Another vital type is Signals Intelligence (SIGINT), which focuses on intercepting and analyzing communications between enemy forces. This form of intelligence is crucial for understanding the intentions and capabilities of adversaries. By monitoring radio transmissions, satellite systems can detect patterns in communication that might indicate an impending attack or troop movements. Imagine SIGINT as a whispering wind, carrying secrets across the battlefield, allowing military leaders to anticipate and counter enemy actions effectively.
Additionally, Electronic Intelligence (ELINT) comes into play, which involves the collection of data from electronic signals emitted by radar and other systems. ELINT helps military forces understand the electronic landscape of their operational environment, identifying threats from missile systems or radar installations. The fusion of IMINT, SIGINT, and ELINT creates a comprehensive intelligence picture that is crucial for informed decision-making.
To illustrate the differences between these types of intelligence, consider the following table:
| Type of Intelligence | Description | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Imagery Intelligence (IMINT) | Visual data captured from satellites | Provides detailed insights into enemy positions and terrain |
| Signals Intelligence (SIGINT) | Intercepting and analyzing communications | Enhances understanding of enemy intentions |
| Electronic Intelligence (ELINT) | Data collection from electronic signals | Identifies threats from radar and missile systems |
In summary, the types of intelligence gathered by satellites—IMINT, SIGINT, and ELINT—are essential components of modern military operations. Each type provides unique insights that, when combined, create a robust intelligence framework. This framework not only aids in tactical planning but also enhances the overall effectiveness of military operations, ensuring that forces remain one step ahead of their adversaries. In a world where information is power, the ability to gather and analyze this intelligence can be the difference between victory and defeat.
- What is the primary function of satellite intelligence in warfare?
Satellite intelligence primarily functions to provide real-time data that enhances situational awareness, informs strategic planning, and supports coordinated military operations. - How does imagery intelligence differ from signals intelligence?
Imagery intelligence focuses on visual data captured from satellites, while signals intelligence involves intercepting and analyzing communications. - What challenges do satellites face in gathering intelligence?
Satellites face challenges such as vulnerability to cyberattacks and limitations imposed by adverse weather conditions, which can affect data accuracy and availability.
Imagery Intelligence (IMINT)
Imagery Intelligence, commonly known as IMINT, plays a pivotal role in modern military operations. Imagine being able to see the battlefield from above, gaining a bird's-eye view of enemy positions, terrain features, and even troop movements. This is precisely what IMINT offers, transforming the way military strategists plan and execute their missions. By utilizing advanced satellite technology, military forces can capture high-resolution images that provide critical insights into the operational landscape.
The power of IMINT lies in its ability to deliver detailed visual data that can be analyzed for strategic decision-making. For instance, during reconnaissance missions, IMINT allows commanders to assess potential threats and identify key targets. This visual intelligence is invaluable, especially in dynamic combat scenarios where ground conditions may change rapidly. With the aid of sophisticated imaging techniques, such as synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and electro-optical sensors, military personnel can obtain real-time imagery that enhances situational awareness and operational effectiveness.
Moreover, the integration of IMINT with other forms of intelligence, such as Signals Intelligence (SIGINT) and Human Intelligence (HUMINT), creates a comprehensive picture of the battlefield. This layered approach to intelligence gathering enables military planners to formulate more effective strategies and anticipate enemy actions. For example, by analyzing satellite imagery alongside intercepted communications, analysts can pinpoint not only where enemy forces are located but also their potential intentions and capabilities.
However, the use of IMINT is not without challenges. Factors such as adverse weather conditions and the need for timely updates can complicate the intelligence-gathering process. For instance, cloud cover can obscure satellite imagery, making it difficult to obtain accurate assessments of ground conditions. To mitigate these challenges, military organizations continually invest in improving satellite technology and data processing techniques, ensuring that IMINT remains a reliable source of intelligence.
In summary, Imagery Intelligence (IMINT) is a cornerstone of modern military operations, providing essential visual data that enhances decision-making and operational planning. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of IMINT will likely expand, offering even greater insights into the complexities of warfare. The future of military strategy will undoubtedly be shaped by the ongoing evolution of satellite-based imagery intelligence.
Signals Intelligence (SIGINT)
Signals Intelligence, commonly referred to as SIGINT, is a pivotal aspect of modern military operations, acting as the ears and eyes of intelligence agencies. Imagine being able to listen in on the conversations of your adversaries; that’s the essence of SIGINT. It involves the interception and analysis of various forms of communication, including radio, telephone, and internet traffic. In a world where information is power, SIGINT provides a significant advantage on the battlefield.
At its core, SIGINT is about gathering actionable intelligence from the electromagnetic spectrum. This intelligence can be categorized into two primary types: communication intelligence (COMINT) and electronic intelligence (ELINT). COMINT focuses on the interception of voice and data communications, while ELINT deals with the detection and analysis of non-communication signals, such as radar emissions. Together, they create a comprehensive picture of enemy movements and intentions.
One of the most compelling aspects of SIGINT is its ability to enhance situational awareness. Imagine a military commander who can anticipate enemy actions based on real-time intercepted communications. This capability allows for preemptive strikes and informed decision-making, ultimately leading to operational superiority. For instance, if SIGINT reveals that enemy troops are preparing for an attack, commanders can reposition their forces or bolster defenses accordingly.
Moreover, SIGINT is not just limited to military applications; it plays a crucial role in national security as well. Intelligence agencies utilize SIGINT to monitor potential threats, track terrorist activities, and safeguard national interests. The information gathered can be vital for diplomatic negotiations and counter-terrorism operations, showcasing the extensive reach of SIGINT beyond the battlefield.
However, the effectiveness of SIGINT is not without its challenges. The rapid advancement of technology means that adversaries are also becoming adept at countering SIGINT efforts. Encryption and secure communication methods can make it increasingly difficult to intercept valuable information. Therefore, military and intelligence organizations must continuously evolve their strategies and technologies to stay ahead in the SIGINT game.
In conclusion, Signals Intelligence is a game-changer in modern warfare. It transforms the way military operations are conducted by providing critical insights that shape strategies and tactics. As technology continues to advance, the importance of SIGINT will only grow, making it an indispensable tool for military forces around the globe.
- What is the primary function of Signals Intelligence (SIGINT)?
SIGINT primarily focuses on intercepting and analyzing communications to gather intelligence on enemy activities and intentions. - How does SIGINT enhance military operations?
By providing real-time information, SIGINT allows military commanders to make informed decisions, anticipate enemy actions, and improve situational awareness. - What types of signals are intercepted in SIGINT?
SIGINT encompasses communication signals (COMINT) and electronic signals (ELINT), each providing unique insights into enemy capabilities. - What challenges does SIGINT face?
Challenges include advancements in encryption and secure communications by adversaries, making it harder to intercept valuable information.
Integration with Ground Forces
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern warfare, the integration of satellite intelligence with ground forces has become a game-changer. Imagine a chess match where one player has a bird's-eye view of the entire board while the other is limited to their immediate surroundings. This analogy perfectly encapsulates how satellite technology enhances the operational effectiveness of ground troops. By providing real-time data, satellites enable commanders and soldiers to make informed decisions that can significantly alter the course of a mission.
When ground forces receive timely intelligence from satellites, they can execute their strategies with a level of precision that was previously unattainable. For instance, if a battalion is tasked with advancing towards a target, satellite imagery can reveal enemy positions, terrain challenges, and even potential ambush sites. This information allows commanders to devise tactics that minimize risks and maximize the chances of success. The ability to adapt on the fly, based on real-time updates, is akin to having a GPS system guiding you through a complex maze.
Moreover, the integration doesn't stop at just receiving data; it's about how that data is communicated and utilized on the ground. With advanced communication systems, soldiers can access satellite feeds directly on their devices, whether it's a rugged tablet or a specialized headset. This immediate access to intelligence fosters a culture of collaboration among units, as they can share insights and coordinate movements seamlessly. Picture a team of dancers performing a synchronized routine; every member knows their role and timing, which is crucial for achieving harmony and success.
However, this integration also poses challenges. For instance, the reliance on technology means that ground forces must be trained not only in combat skills but also in technological proficiency. They need to understand how to interpret satellite data and integrate it into their tactical planning. This training is essential for ensuring that the full potential of satellite intelligence is realized on the battlefield.
In summary, the integration of satellite intelligence with ground forces is a vital component of modern military operations. It enhances situational awareness, improves decision-making, and ultimately increases the effectiveness of combat missions. As technology continues to advance, we can expect this integration to become even more sophisticated, paving the way for a new era of warfare where information superiority is the key to victory.
Challenges in Satellite Intelligence
While satellite intelligence has revolutionized modern warfare, it is not without its challenges. The reliance on these high-tech tools introduces a range of vulnerabilities that can impact military operations significantly. One of the most pressing challenges is the risk of cybersecurity threats. As military forces increasingly depend on satellite communications for real-time data, they also expose themselves to potential cyberattacks. Adversaries are constantly developing sophisticated methods to intercept or disrupt satellite signals, which can lead to critical information being compromised or rendered inaccessible. This situation underscores the necessity for robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard satellite operations and maintain the integrity of military intelligence.
Another significant hurdle faced by satellite intelligence is the impact of adverse weather conditions. Satellites, while designed to operate in a variety of environments, can still be affected by severe weather phenomena such as storms, heavy cloud cover, or atmospheric disturbances. These conditions can hinder the ability of satellites to gather accurate data, leading to potential gaps in intelligence that could be detrimental during critical operations. For instance, a reconnaissance mission that relies on satellite imagery may be severely compromised if the satellite is unable to capture clear visuals due to cloud cover. To mitigate these effects, military organizations are investing in advanced technologies and strategies that enhance data collection capabilities, even under less-than-ideal weather conditions.
Moreover, the physical vulnerabilities of satellites themselves pose a challenge. Satellites can be targeted by anti-satellite weapons or experience malfunctions due to space debris, which can disrupt their functionality. The loss of a single satellite could severely impact a military's operational capabilities, making it essential for defense forces to develop contingency plans and alternative systems to ensure continuity of intelligence operations.
In summary, while satellite intelligence offers unparalleled advantages in modern warfare, it is crucial to address the challenges it faces. By understanding and mitigating the risks associated with cybersecurity threats, weather limitations, and physical vulnerabilities, military forces can enhance their operational effectiveness and maintain a strategic edge on the battlefield.
- What are the main challenges faced by satellite intelligence? The main challenges include cybersecurity threats, adverse weather conditions, and physical vulnerabilities of satellites.
- How do cybersecurity threats impact satellite operations? Cybersecurity threats can lead to interception or disruption of satellite signals, compromising critical military information.
- Can weather conditions affect satellite data collection? Yes, severe weather can hinder satellite functionality and data accuracy, impacting reconnaissance missions.
- What measures are being taken to secure satellite communications? Military organizations are investing in advanced cybersecurity technologies and strategies to protect satellite operations from potential attacks.
Cybersecurity Threats
The rise of satellite technology has revolutionized modern warfare, but with great power comes great responsibility—and vulnerability. Cybersecurity threats pose significant risks to satellite operations, making it imperative for military organizations to prioritize the security of their satellite systems. Imagine a world where an enemy could intercept crucial satellite communications, gaining insights into military strategies and troop movements. This scenario isn't just a plot from a spy novel; it's a real concern for defense agencies worldwide.
As satellites become increasingly integral to military operations, they also become prime targets for cyberattacks. These attacks can range from jamming signals to sophisticated hacking attempts that aim to take control of satellite systems. The implications of such breaches can be catastrophic, potentially leading to misinformation, disrupted communications, and compromised missions. In fact, a successful cyberattack on a satellite could render it useless, leaving ground forces without critical real-time intelligence.
To combat these threats, military organizations are investing heavily in robust cybersecurity measures. These measures include:
- Encryption: Utilizing advanced encryption techniques to secure communications between satellites and ground stations.
- Intrusion Detection Systems: Implementing systems that monitor satellite networks for unusual activity, allowing for quick responses to potential breaches.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting frequent audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure that all systems are up to date with the latest security protocols.
Moreover, collaboration with private tech companies and cybersecurity experts is becoming increasingly common. By leveraging the expertise of those on the cutting edge of technology, military forces can enhance their defenses against potential cyber threats. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in cybersecurity measures is also a game changer, enabling faster detection and response to anomalies that could indicate a cyberattack.
In conclusion, as satellite technology continues to evolve, so too must the strategies to protect it. Cybersecurity is not just an IT issue; it's a critical component of national security. The ability to safeguard satellite communications will determine the effectiveness of military operations in the future. As we look ahead, the question remains: will we be able to outsmart our adversaries in the cyber realm as effectively as we do on the battlefield?
Weather Limitations
When we think about the incredible capabilities of satellites, it’s easy to get lost in the awe of technology. However, the harsh reality is that can significantly impact satellite functionality and the accuracy of the data they provide. Imagine trying to take a clear photograph on a foggy day; the same principle applies to satellites orbiting our planet. Various weather conditions can obstruct or distort the signals that satellites rely on, leading to gaps in intelligence that could be critical in military operations.
For instance, heavy rain, snow, and cloud cover can interfere with the signals sent and received by satellites, reducing the quality of imagery intelligence (IMINT). It’s like trying to tune into your favorite radio station during a thunderstorm—static and interruptions can make it nearly impossible to get a clear signal. This interference can lead to delayed responses in military operations, potentially allowing adversaries to exploit these windows of opportunity.
Moreover, the effects of weather are not just limited to image quality. Signals intelligence (SIGINT) can also be affected. When storms brew, the electromagnetic spectrum can become chaotic, causing distortions in communication signals. This can hinder the ability to intercept and analyze critical enemy communications, leading to a lack of situational awareness on the battlefield. In such scenarios, military leaders might find themselves operating in the dark, making decisions based on incomplete or outdated information.
To combat these weather-induced challenges, military forces often employ a variety of strategies:
- Redundancy in Satellite Systems: Utilizing multiple satellites can help ensure that if one is compromised by weather, others can still provide the necessary data.
- Advanced Imaging Technologies: Some satellites are equipped with technologies that allow them to see through clouds or other obstructions, such as synthetic aperture radar (SAR).
- Real-Time Data Fusion: Integrating data from various sources, including ground-based sensors and aerial reconnaissance, can help fill in the gaps caused by poor satellite performance.
In conclusion, while satellite technology has revolutionized modern warfare, it is essential to recognize and address the limitations imposed by weather conditions. As military operations become increasingly dependent on real-time intelligence, understanding these challenges will be crucial for enhancing operational effectiveness and maintaining a strategic edge over adversaries.
Q: How do weather conditions affect satellite imagery?
A: Weather conditions such as clouds, rain, and snow can obscure satellite imagery, reducing the clarity and accuracy of the data collected.
Q: What technologies do satellites use to overcome weather limitations?
A: Some satellites utilize synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and other advanced imaging technologies that can penetrate cloud cover and provide clearer data.
Q: Why is real-time data fusion important in military operations?
A: Real-time data fusion allows military forces to integrate information from various sources, compensating for any gaps caused by weather-related satellite issues.
Future of Satellite Warfare
The future of warfare is poised to undergo a dramatic transformation, heavily influenced by advancements in satellite technology. As we look ahead, it becomes increasingly clear that satellites will not merely be tools for observation but will evolve into integral components of military strategy. Imagine a battlefield where every move is tracked in real-time, where commanders can make split-second decisions based on precise data streamed directly from orbit. This is not a distant dream; it's the emerging reality of modern warfare.
One of the most exciting prospects is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with satellite systems. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data faster than any human could, identifying patterns and anomalies that might indicate enemy movements or potential threats. This capability allows military strategists to anticipate actions and respond proactively, rather than reactively. As AI continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more sophisticated systems capable of not just gathering data, but also providing actionable insights that could change the course of engagements.
Moreover, the rise of miniaturized satellites is set to revolutionize how we approach satellite warfare. These smaller, more cost-effective satellites can be deployed in swarms, offering redundancy and resilience in intelligence-gathering operations. Picture a network of tiny satellites working together, forming a comprehensive surveillance web that can cover vast areas, making it nearly impossible for adversaries to hide. This concept of swarm intelligence could redefine the rules of engagement, as military forces gain unprecedented situational awareness.
However, with these advancements come challenges. The arms race in space is intensifying, with nations investing heavily in counter-satellite technologies. The potential for anti-satellite weapons poses significant risks, as adversaries could target critical satellite infrastructure, disrupting communication and intelligence flows. Therefore, securing satellite networks against such threats will be paramount. This includes not only physical protection but also enhancing cybersecurity measures to safeguard against hacking and electronic warfare tactics.
Furthermore, as we delve deeper into the future, we must consider the ethical implications of using satellites in warfare. The ability to conduct precision strikes based on satellite data raises questions about accountability and the potential for collateral damage. Military forces must navigate these complex moral landscapes while striving to utilize technology responsibly.
In conclusion, the future of satellite warfare is an exciting yet complex landscape filled with opportunities and challenges. As technology continues to advance, the integration of AI, miniaturized satellites, and enhanced cybersecurity measures will shape how military operations are conducted. The key to success will lie in adapting to these changes while maintaining a strong ethical framework to guide the application of satellite intelligence in warfare.
- What role do satellites play in modern warfare? Satellites provide critical real-time intelligence, enhancing situational awareness and enabling strategic decision-making.
- How does AI impact satellite operations? AI can analyze large datasets quickly, offering insights that improve military responsiveness and operational effectiveness.
- What are the risks associated with satellite warfare? Risks include vulnerability to cyberattacks, anti-satellite weapons, and ethical concerns regarding the use of precision targeting.
- What is swarm intelligence in satellite technology? Swarm intelligence refers to the use of multiple small satellites working together to create a comprehensive surveillance network.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What role do satellites play in modern warfare?
Satellites are crucial for providing real-time intelligence, enhancing military operations, and improving strategic planning. They enable forces to gather immediate data about enemy movements and terrain, which can significantly influence decision-making and operational effectiveness.
-
What types of intelligence can satellites collect?
Satellites gather various types of intelligence, including Imagery Intelligence (IMINT), which captures visual data, and Signals Intelligence (SIGINT), which focuses on intercepting communications. Each type contributes uniquely to shaping military strategies and tactics.
-
How does satellite intelligence integrate with ground forces?
Integration is key! Real-time data from satellites enhances battlefield communication and aids tactical maneuvers, allowing ground forces to operate more effectively and coordinate their actions based on the latest intelligence.
-
What challenges do satellites face in military applications?
Despite their advantages, satellite intelligence encounters challenges such as vulnerability to cyberattacks and limitations due to adverse weather conditions. These factors can hinder data accuracy and the functionality of satellite operations.
-
How do cybersecurity threats affect satellite operations?
Cybersecurity threats pose significant risks as adversaries can target satellite communications. Securing these systems is essential to maintain operational integrity and protect sensitive military data.
-
What impact do weather conditions have on satellite functionality?
Adverse weather can disrupt satellite signals and affect data collection accuracy. Military operations often need to adapt strategies to account for these weather-related challenges, ensuring reliable intelligence is still gathered.
-
What does the future hold for satellite technology in warfare?
The future of warfare is likely to see an increased reliance on advanced satellite technology, with emerging trends and innovations shaping military operations. This could include improved data collection methods and enhanced security measures.